





ADHD affects up to 10% of people worldwide, and yet there is still a lot of misconceptions around it.
Here we discuss 5 common misconceptions about ADHD:
- Because ADHD comes from the brain developing in an atypical way, there is no age too young or too old to be diagnosed.
- In most cases, ADHD symptoms will persist throughout the person’s life.
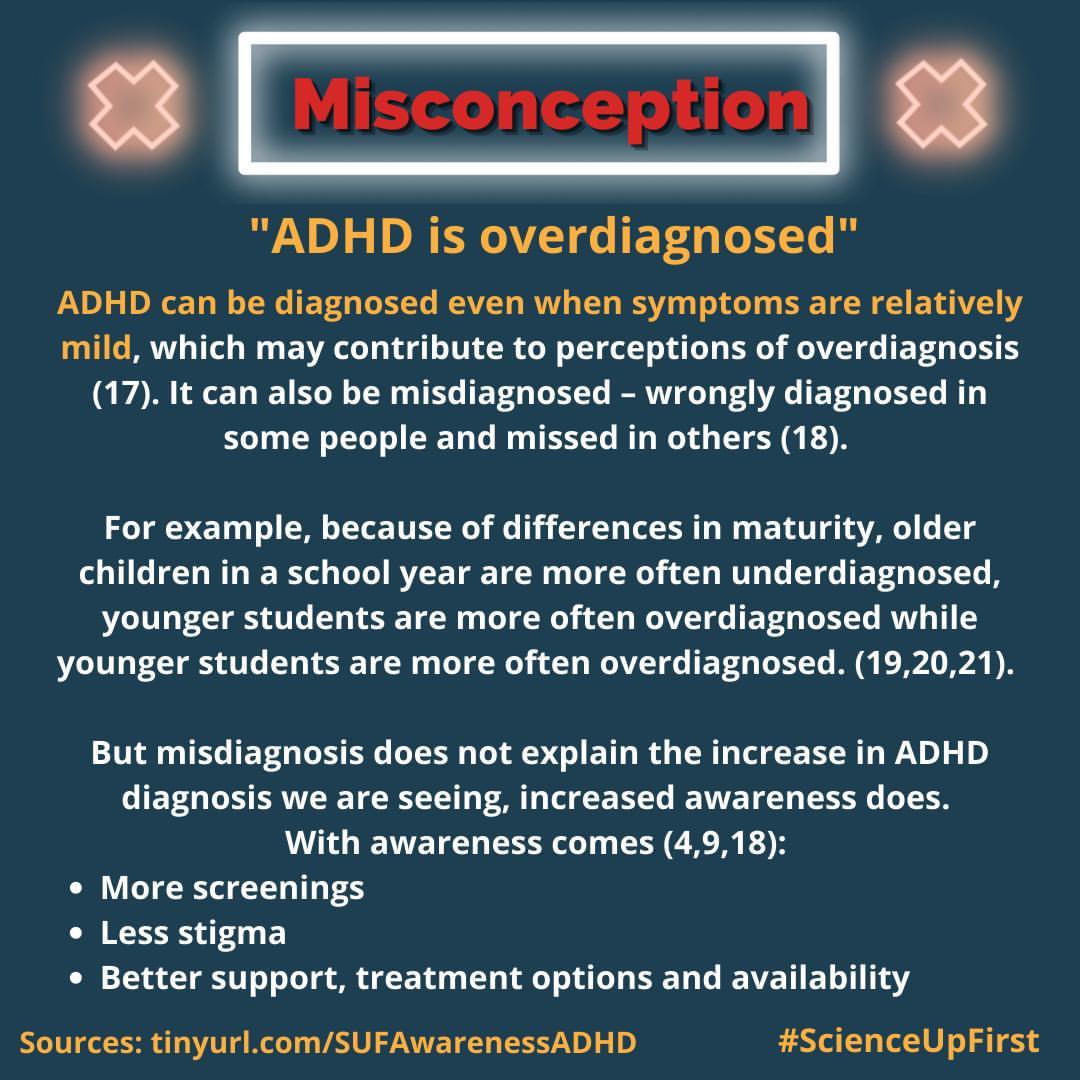
- People think ADHD is overdiagnosed, but it’s more complicated than that.
- People with ADHD are not lazy. Poor executive functioning and having a hard time focusing on tedious non-stimulating tasks can make them seem like they are unmotivated or uninterested.
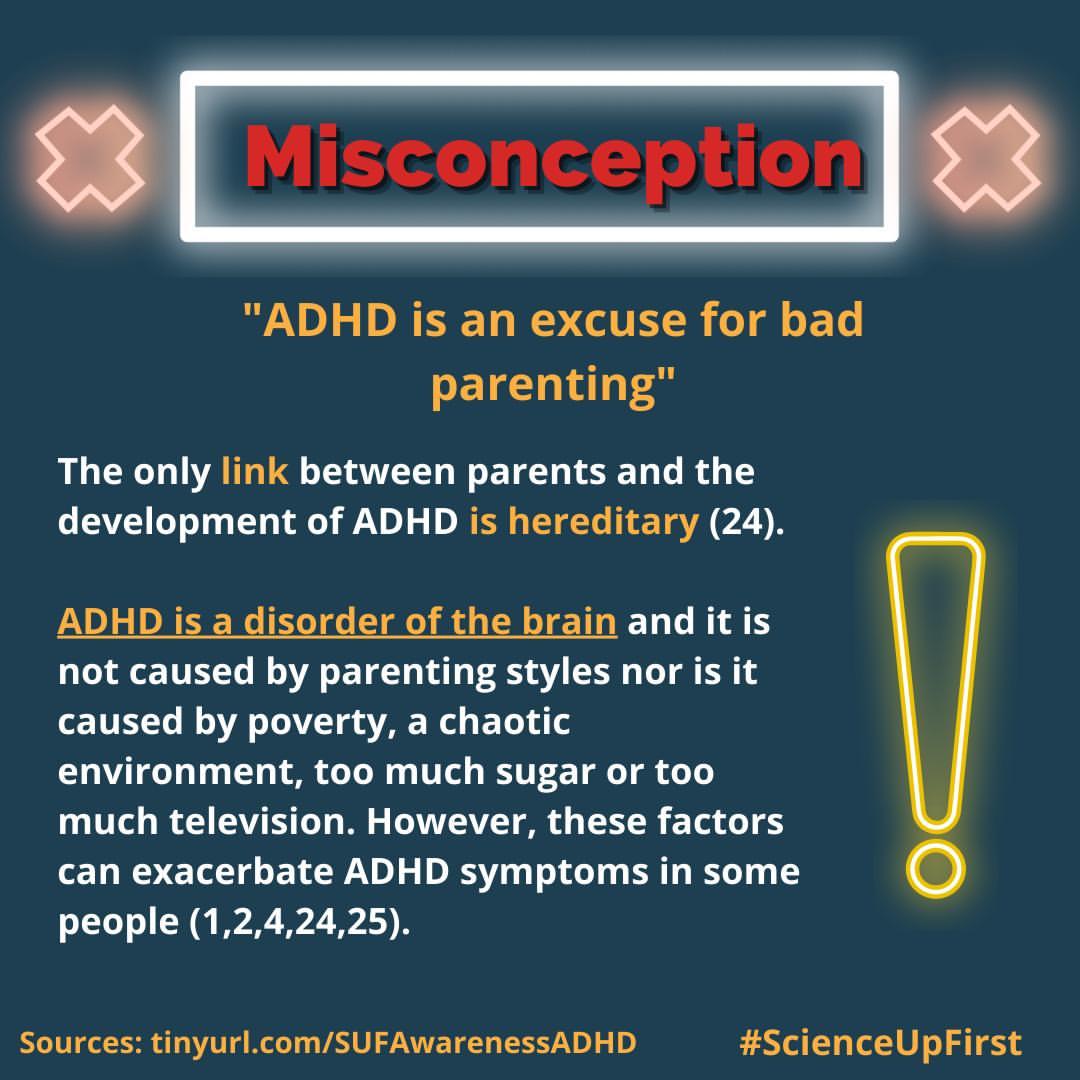
- Parenting style has nothing to do with the development of ADHD
Among others, these misconceptions can prevent people with ADHD from reaching their full potential. Undiagnosed and untreated ADHD can cause major life impairments, such as financial, work, health and relationship difficulties.
Share this post with your friends and family. Together, let’s increase awareness on ADHD and put these misconceptions away for good!
Share our original Tweet!
Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) affects up to 10% of people worldwide, and yet there is still a lot of misconceptions around it.
Let’s look at 5 common misconceptions about ADHD #ScienceUpFirst
[1/14] pic.twitter.com/SVM18QkRGw
— ScienceUpFirst | LaScienced’Abord (@ScienceUpFirst) October 20, 2022
View our original Instagram Post!
View this post on Instagram
- What is ADHD?
- About ADHD – Symptoms, Causes and Treatment
- Are you born with ADHD? What you should know
- Causes of ADHD: What We Know Today
- Parenting Behavior Mediates the Intergenerational Association of Parent and Child Offspring ADHD Symptoms
- Biological and rearing mother influences on child ADHD symptoms: revisiting the developmental interface between nature and nurture
- Is Adult ADHD a Childhood-Onset Neurodevelopmental Disorder? Evidence From a Four-Decade Longitudinal Cohort
- 8 ADHD Myths & Misconceptions
- Myths and Misunderstandings
- Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in children – Symptoms and causes
- Predictors of persistent ADHD: An 11-year follow-up study
- Evaluation of the Persistence, Remission, and Emergence of Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder in Young Adulthood
- Persistence and remission of ADHD during adulthood: a 7-year clinical follow-up study
- Diagnosis of ADHD in Adults
- Adult attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) – Symptoms and causes
- Functional Impairments in Adults With Self-Reports of Diagnosed ADHD: A Controlled Study of 1001 Adults in the Community
- Overdiagnosis of Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder in Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Scoping Review
- The Myth of ADHD Overdiagnosis
- Association of Relative Age in the School Year With Diagnosis of Intellectual Disability, Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder, and Depression
- Influence of relative age on diagnosis and treatment of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in children
- The Combined Effects of Young Relative Age and Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder on Negative Long-term Outcomes
- Experiences of criticism in adults with ADHD: A qualitative study
- ADHD and Low Motivation: What’s Really Going On?
- General Info
- Parenting a Child with ADHD
- General Prevalence of ADHD
- The Worldwide Prevalence of ADHD: A Systematic Review and Metaregression Analysis
- Depression and other correlates of adult Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) symptoms among Hungarian university students
- Long-Term Outcomes of ADHD: A Systematic Review of Self-Esteem and Social Function




