

It can be unsettling when a trusted health organization shares something that doesn’t match other evidence. But you’re not powerless. Taking a moment to pause, slow down, look closer, and think critically helps you get a clearer picture, just like you would with any other source.
When something feels off, checking other reputable sources and seeing what experts in the field agree on can help you understand what the evidence actually supports.
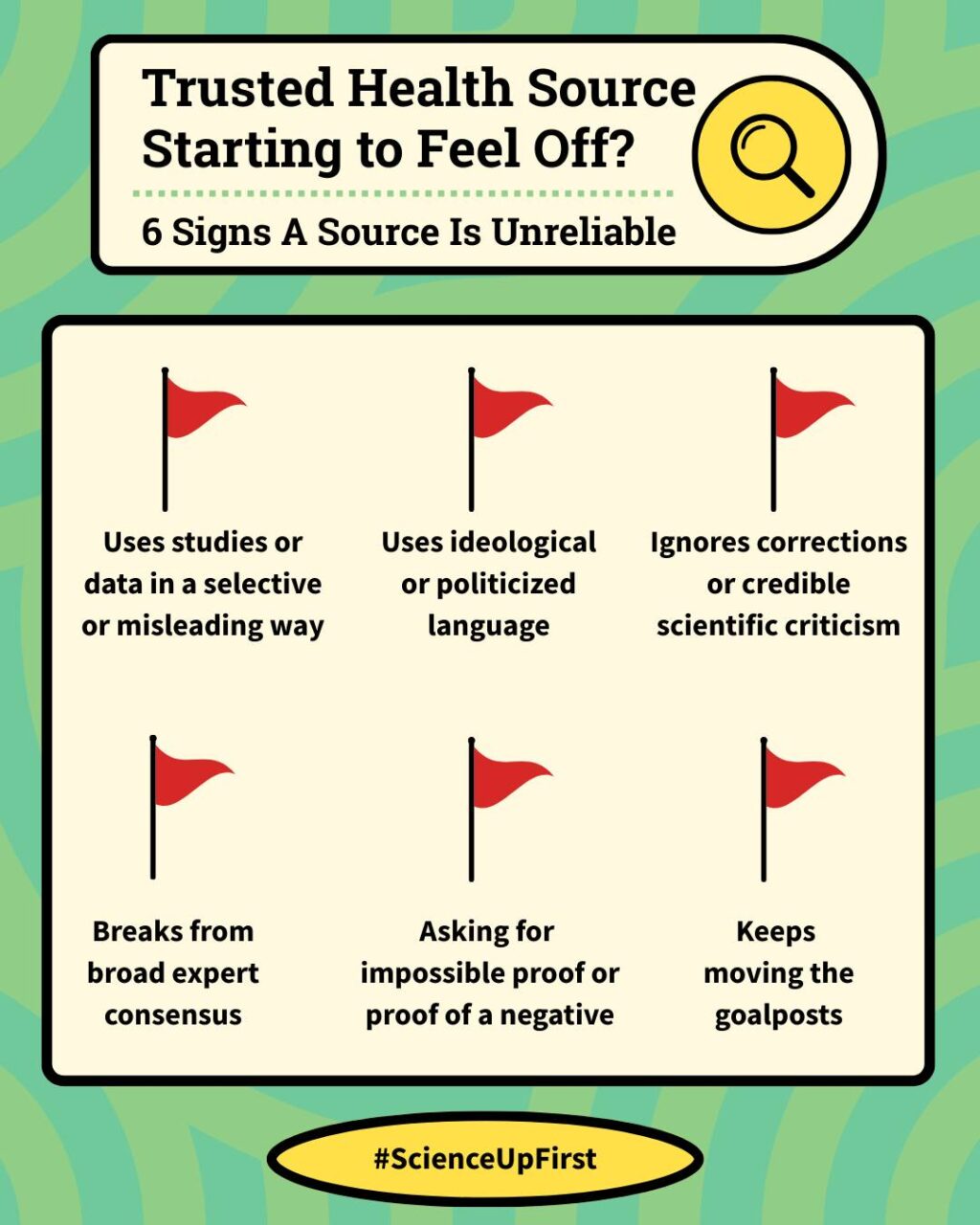
Evidence is still your best guide. Science is built on many voices, not one institution. And a single surprising statement, even from a familiar or historically trusted source, doesn’t replace the wider consensus.
Resources
How is a scientific consensus reached? | ScienceUpFirst | November 2023
Misinformer Tactic: Cherry Picking | ScienceUpFirst | May 2024
Moving the Goalposts | Logically Fallacious
The Fallacy of ‘Moving the Goalposts’, Explained | Snopes | February 2023
Proving Non-Existence | Logically Fallacious
Share our original Bluesky Post!
Science is built on many voices, not one institution. A single surprising statement, even from a familiar or historically trusted source, doesn’t replace the wider consensus. But how to gauge reliability?👇 scienceupfirst.com/misinformati… #ScienceUpFirst
— ScienceUpFirst (@scienceupfirst.bsky.social) December 10, 2025 at 1:14 PM
[image or embed]
View our original Instagram Post!